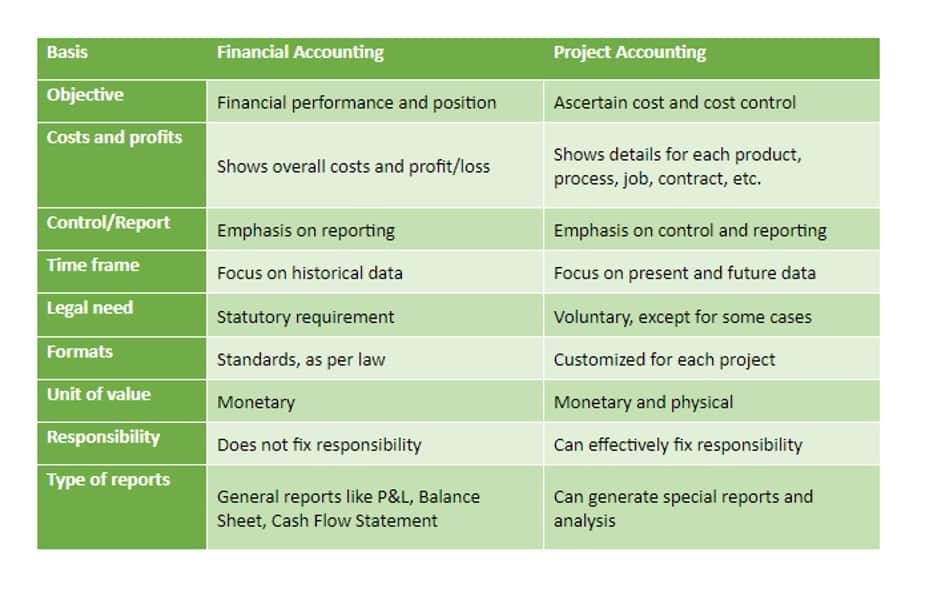
The amount of short-term debt as compared to long-term debt is important when analyzing a company’s financial health. For example, let’s say that two companies in the same industry might have the same amount of total debt. High levels of current liabilities can negatively impact a company’s profitability due to high-interest payments on debts or other obligations. Companies should strive to keep their total amount of current liabilities as low as possible in order to remain profitable. A current liability is an amount owed by a company to its creditors that must be paid within one year or the normal operating cycle, whichever is longer.
We and our partners process data to provide:
The current ratio measures a company’s ability to pay its short-term financial debts or obligations. It shows investors and analysts whether a company has enough current assets on its balance sheet to satisfy or pay off its current debt and other payables. Current liabilities are a company’s short-term financial obligations that are due within one year or within a normal operating cycle.
This is because cash on hand today can be invested and thus can grow to a greater future amount. Long-term liabilities are those liabilities that will not be satisfied within one year or the operating cycle, if longer than one year. Included in this category are Mortgages Payable, Bonds Payable, and Lease Obligations. Income taxes are required to be withheld from an employee’s salary for payment to a federal, state, or local authority (hence they are known as withholding taxes).
However, if one company’s debt is mostly short-term debt, it might run into cash flow issues if not enough revenue is generated to meet its obligations. The good news is cash and cash equivalents cce definition that for a loan such as our car loan or even a home loan, the loan is typically what is called fully amortizing. For example, your last (sixtieth) payment would only incur $3.09 in interest, with the remaining payment covering the last of the principle owed. Interest is an expense that you might pay for the use of someone else’s money.
This method was more commonly used prior to the ability to do the calculations using calculators or computers, because the calculation was easier to perform. However, with today’s technology, it is more common to see the interest calculation performed using a 365-day year. Noncurrent liabilities are long-term obligations with payment typically due in a subsequent operating period.
Why You Can Trust Finance Strategists
Sometimes, companies use an account called other current liabilities as a catch-all line item on their balance sheets to include all other liabilities due within a year that are not classified elsewhere. A note payable is usually classified as a long-term (noncurrent) liability if the note period is longer than one year or the standard operating period of the company. However, during the company’s current operating period, any portion of the long-term note due that will be paid in the current period is considered a current portion of a note payable.
The basics of shipping charges and credit terms were addressed in Merchandising Transactions if you would like to refresh yourself on the mechanics. Also, to review accounts payable, you can also return to Merchandising Transactions for detailed explanations. For example, assume the owner of a clothing boutique purchaseshangers from a manufacturer on credit.
The former is the result of actions undertaken to raise funding to grow the business, while the latter is the byproduct of obligations arising from normal business operations. Having an optimal amount of current assets on hand to cover current liabilities is essential to having a healthy cash flow. Ideally, suppliers would like shorter terms so that they’re paid sooner rather than later—helping their cash flow.
Get in Touch With a Financial Advisor
Accounts payable accounts for financial obligations owed to suppliers after purchasing products or services on credit. This account may be an open credit line between the supplier and the company. An open credit line is a borrowing agreement for an amount of money, supplies, or inventory. The option to borrow from the lender can be exercised at any time within the agreed time period. Accounts payable accounts for financialobligations owed to suppliers after purchasing products or serviceson credit. An open credit line is a borrowingagreement for an amount of money, supplies, or inventory.
Would you prefer to work with a financial professional remotely or in-person?
For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) hasworked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online. For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) has worked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online. A financial professional will offer guidance based on the information provided and offer a no-obligation call to better understand your situation. Someone on our team will connect you with a financial professional in our network holding the correct designation and expertise. Our writing and editorial staff are a team of experts holding advanced financial designations and have written for most major financial media publications. Our work has been directly cited by organizations including Entrepreneur, Business Insider, Investopedia, Forbes, CNBC, which transactions affect retained earnings and many others.
- At first, start-ups typically do not create enough cash flow to sustain operations.
- Having an optimal amount of current assets on hand to cover current liabilities is essential to having a healthy cash flow.
- As soon as the companyprovides all, or a portion, of the product or service, the value isthen recognized as earned revenue.
- Because part of the service will be provided in 2019 and the rest in 2020, we need to be careful to keep the recognition of revenue in its proper period.
- Current assets include cash or accounts receivable, which is money owed by customers for sales.
- Income taxes are discussed in greater detail inRecord Transactions Incurred in Preparing Payroll.
Current liabilities are reported on the classified balance sheet, listed before noncurrent liabilities. Changes in current liabilities from the beginning of an accounting period to the end are reported on the statement of cash flows as part of the cash flows from operations section. An increase in current liabilities over a period increases cash flow, while a decrease in current liabilities decreases cash flow. A current liability is a debt or obligation due within a company’s standard operating period, typically a year, although there are exceptions that are longer or shorter than a year. This method assumes a twelve-monthdenominator in the calculation, which means that we are using thecalculation method based on a 360-day year. This method was morecommonly used prior to the ability to do the calculations usingcalculators or computers, because the calculation was easier toperform.
Current Liabilities Put Simple
Taxes payable refers to a liability createdwhen a company collects taxes on behalf of employees and customersor for tax obligations owed by the company, such as sales taxes orincome taxes. For example, assume that each time a shoe store sells a $50 pair of shoes, it will charge the customer a sales tax of 8% of the sales price. The $4 sales tax is a current liability until distributed within the company’s operating period to the government authority collecting sales tax. The customer’s advance payment for landscaping is recognized in the Unearned Service Revenue account, which is a liability. Once the company has finished the client’s landscaping, it may recognize all of the advance payment as earned revenue in the Service Revenue account. If the landscaping company provides part of the landscaping services within the operating period, it may recognize the value of the work completed at that time.
The annual interest rate is 3%, and you are required tomake scheduled payments each month in the amount of $400. You firstneed to determine the monthly interest rate by dividing 3% bytwelve months (3%/12), which is 0.25%. The monthly interest rate of0.25% is multiplied by the outstanding principal balance of $10,000to get an interest expense of $25.
Terms of the loan require equal annual principal repayments of $10,000 for the next ten years. Even though the overall $100,000 note payable is considered long term, the $10,000 required repayment during the company’s operating cycle is considered current (short term). This means $10,000 would be classified as the current portion of a noncurrent note payable, and the remaining $90,000 would remain a noncurrent note payable. For example, a bakery company may need to take out a $100,000loan to continue business operations. Terms of the loan require equal annualprincipal repayments of $10,000 for the next ten years.
When the company pays its balance due to suppliers, it debits accounts payable and credits cash for $10 million. In addition to the $18,000 portion of the note payable that will be paid in the current year, any accrued interest on both the current portion and the long-term portion of the note payable that is due will also be paid. Assume, for example, that for the current year $7,000 of interest will be accrued. In the current year the debtor will pay a total of $25,000—that is, $7,000 in interest and $18,000 for the current portion of the note payable. Proper reporting of current liabilities helps decision-makers understand a company’s burn rate and how much cash is needed for the company to meet its short-term and long-term cash obligations. If misrepresented, the cash needs of the company may not be met, and the company can quickly go out of business.